Object Segmentation by Oriented Image Foresting Transform with Connectivity Constraints
Ph.D. student: Lucy A. C. MansillaSupervisor: Paulo A. V. Miranda
This work corresponds to the thesis presented to the Institute of Mathematics and Statistics of the University of São Paulo (IME-USP) to obtain a Ph.D. degree in computer science. The complete text is available here.
Abstract
Object segmentation is one of the most fundamental and
challenging problems in image processing and computer vision.
The high-level and specific knowledge of the user is often required in
the segmentation process,
due to the presence of heterogeneous backgrounds,
objects with poorly defined boundaries,
field inhomogeneity, noise, artifacts, partial volume effects and
their joint effects.
Global properties of the object of interest, such as
connectivity, shape constraints and boundary polarity,
are useful high-level priors for its segmentation,
allowing the customization of the segmentation for a given target object.
In this work,
we introduce a new method called
Connected Oriented Image Foresting Transform (COIFT),
which provides global optimal solutions according to
a graph-cut measure in graphs,
subject to the connectivity constraint in
the Oriented Image Foresting Transform (OIFT),
in order to ensure the generation of connected objects,
as well as allowing the simultaneous control of the boundary polarity.
While the use of connectivity constraints in other frameworks,
such as in the min-cut/max-flow algorithm,
leads to a NP-Hard problem,
COIFT retains the low computational cost of the OIFT.
Experiments show that COIFT can considerably improve
the segmentation of objects with thin and elongated parts,
for the same number of seeds
in segmentation based on markers.
Datasets
To evaluate our proposed method we designed three new ground truth datasets from 280 public images [1], which contain objects with thin and elongated parts:
-
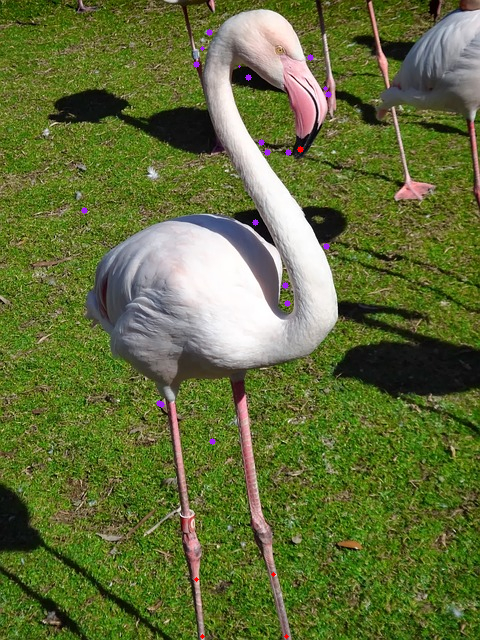
The first dataset is composed of 50 images of birds,
which is available
here.
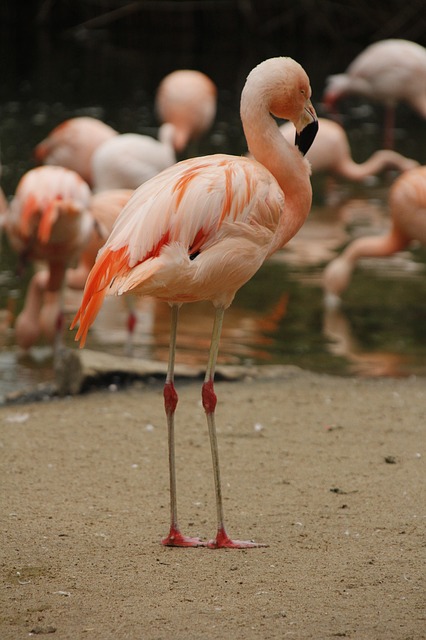

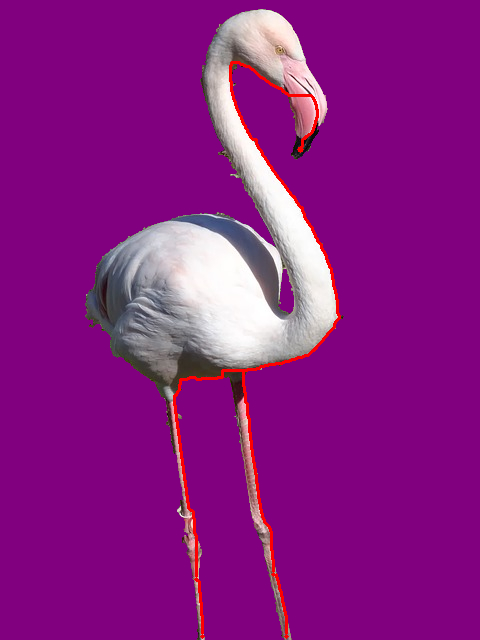
Fig1: Image A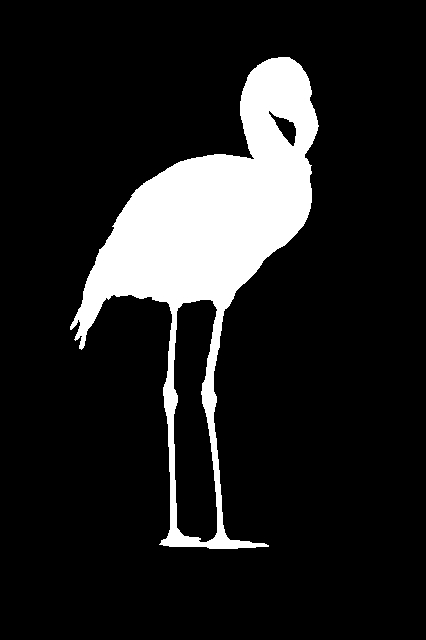 
Fig2: Ground truth of image A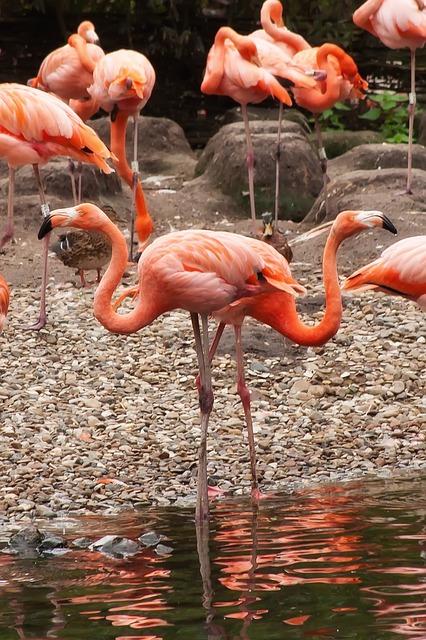 
Fig3: Image B 
Fig4: Ground truth of image B - The second dataset is composed of 100 images of birds,
which is available
here.

Fig5: Image C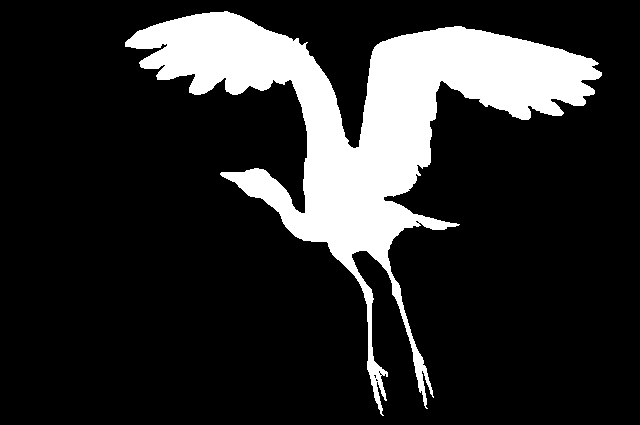 
Fig6: Ground truth of image C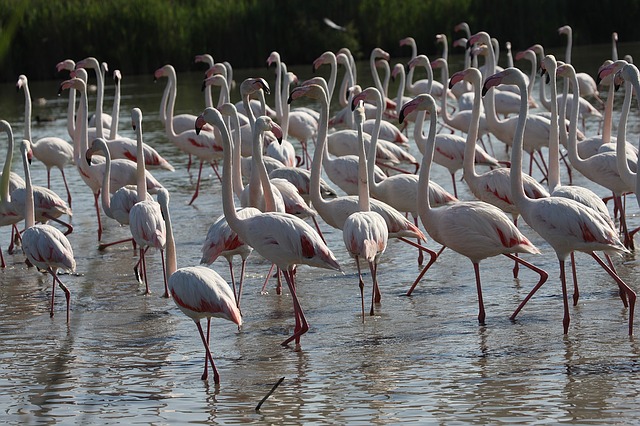 
Fig7: Image D 
Fig8: Ground truth of image D - The third dataset is composed of 130 images of spiders, insects and other invertebrates,
which is available
here.
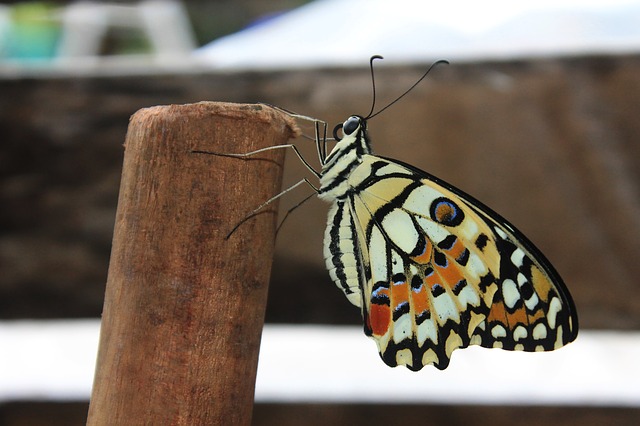

Fig9: Image E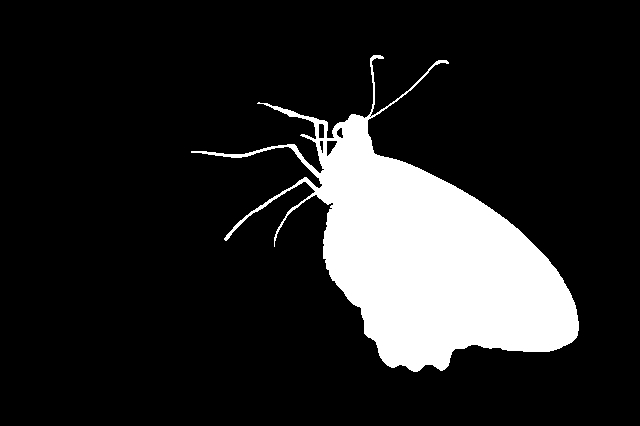 
Fig10: Ground truth of image E 
Fig11: Image F 
Fig12: Ground truth of image F
The first dataset was used in the following scientific publication of the method Connected Oriented Image Foresting Transform (COIFT), which extends the previous Oriented Image Foresting Transform (OIFT):
|
|
The second and third datasets were used to evaluate our method considering the handling of ties in its energy formulation, as presented in our thesis work.
Other related publication:
- Lucy A.C. Mansilla, Paulo A.V. Miranda and Fábio A. M. Cappabianco. Oriented Image Foresting Transform Segmentation with Connectivity Constraints, IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Sept 2016, Phoenix, Arizona, USA, pp. 2554-2558.
[1] These images are released under Creative Commons CC0 into the public domain, available at the web site https://pixabay.com/en.


